The Unexplored Potential of CBDV: What Are Its Promising Uses?
🌿 Unlocking the Wonders of CBDv: A Deep Dive into its Effects and Benefits 🚀 As we journey through the vast landscape of cannabinoids, let’s shine
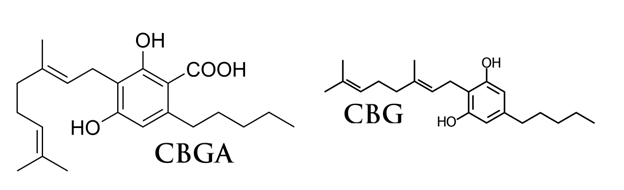
Humans have used Cannabis sativa for centuries, with evidence dating back to the end of the last ice age. As a result, the plant spread across the globe, evolving into a highly diverse species that produces a wide range of chemicals. One of the chemicals, cannabigerol acid (CBGA), is a non-psychotropic (non-intoxicating) phytocannabinoid found in cannabis sativa (fiber variety especially). CBGA and its cannabinoid chemical class type is the second most abundant in the cannabis plant, making up over 16% of the phytocannabinoid content. CBGA is a very important plant metabolite for the synthesis of other phytocannabinoids. CBGA is the precursor to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and numerous other cannabinoids. Since it is the precursor to many of the other phytocannabinoids, Cannabis Sativa creates an abundance of CBGA. Any CBGA that the plant doesn’t convert stays in the plant and can be consumed for its health and wellness benefits, which we’ll discuss later.
In non-psychotropic ‘hemp’ varieties of Cannabis sativa, the plant produces abundant amounts of the major metabolites cannabigerol (CBG) and CBGA. Some hemp strains are primarily CBG/CBGA in comparison to most strains being CBD/CBDA dominant. CBGA is the carboxylic acid form of the phytocannabinoid that occurs naturally similar to THCA or CBDA. During product processing, CBGA is often converted into CBG, but CBGA offers unique medical benefits that are lost once it turns into CBG. The effects of CBGA and CBD in many studies show overlaps in their medicinal effects, indicating a possible common mechanism of action between these two cannabinoids.
All cannabis varieties naturally produce the acidic forms of cannabinoids, like CBGA. That’s what the (A) stands for. The plant doesn’t produce THC, CBD, or CBG as its main products — these are the result of chemical reactions. This process, called decarboxylation, mainly happens with heat or sunlight. Once the temperature hits around 230°F, decarboxylation is almost complete. For THCA, it needs to be decarboxylated into THC to produce its effects when eaten. When vaporized or smoked, THCA instantly decarboxylates at 230°F. But this doesn’t apply to CBGA. Both CBGA and CBG seem to offer unique benefits, even when consumed as an edible. Typically, the ratio of CBGA to CBG is very high, sometimes 10:1. So, in short, CBG is just the decarboxylated form of CBGA.
“People often describe CBGA and CBG as non-psychoactive, and while that’s mostly accurate, it doesn’t tell the whole story. These cannabinoids actively contribute to the entourage effect in cannabis, often adding an energetic lift. A recent study found that CBG significantly modulates the CB2 receptor, though it has a much weaker effect on the CB1 receptor. The CB1 receptor is known for its role in psychoactivity, but CBG’s minimal action there doesn’t make it psychoactive. Instead, it seems to boost THC’s effects. With its stronger action at the CB2 receptor, similar to CBDA and CBD, CBGA/CBG brings some unique benefits.
CBGA/CBG offer similar general benefits similar to CBDA/CBD, this includes the following properties; anti-anxiety, anti-convulsant, anti-inflammatory, anti-nausea, metabolism support, and cardiovascular health support. This is not the only way to look at CBGA/CBG as it is found to have a synergistic effect with other cannabinoids including THC. We will discuss some specific benefits below attributed to CBGA
CBGA has recently become the focus of several clinical studies for its impressive anti-convulsant properties. In one study, researchers tested and compared CBGA, CBDVA, and CBGVA — all cannabinoids known for their anticonvulsant potential. CBGA stood out as the most potent, showing greater effectiveness than CBD in managing seizures. Another study found that CBGA affected key epilepsy-related drug targets in vitro, suggesting the need for further research into its anticonvulsant capabilities. Additionally, CBGA has been shown to enhance the anticonvulsant effects of clobazam in certain types of seizures. The growing body of evidence confirms that CBGA not only has powerful anticonvulsant properties but also interacts with various epilepsy-related drug targets.
Ongoing research has highlighted CBGA’s powerful effects on various metabolic functions. In one study, researchers focused on aldose reductase (ALR2), an enzyme commonly linked to complications in diabetes. CBGA was shown to significantly inhibit ALR2 activity, acting as an enzyme blocker. Additionally, PPARα/γ agonists, which have long been used to treat metabolic diseases, also activate receptors that CBGA targets. Studies suggest CBGA acts as an agonist at these receptors, helping to modulate lipid metabolism. As a dual PPARα/γ agonist, CBGA could enhance therapeutic potential by simultaneously regulating hyperglycemic systems.
Through several modes of action CBGA has shown that it exhibits or has the potential for neuroprotectivity. There is evidence that CBGA, as well as a couple of other cannabinoids, increased the number of viable bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSC), which help with immunomodulation and neuroprotection in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and other neuroimmunological/neurodegenerative diseases. CBGA has also proven to be a potent desensitizer of TRP channels, which play a role in various neurological disorders. While their direct connection to neuroprotection isn’t fully understood, researchers have linked TRPA1 channel activation to Alzheimer’s disease, where it’s thought to regulate astrocyte-mediated inflammation. TRPV1 channel activity is believed to contribute to epilepsy, neuronal excitability, and synaptic transmission. CBGA’s interactions with TRP channels may help improve neurological symptoms in conditions where these channels play a key role in the disease process.
CBGA has been shown to kill cancer cells, especially in colon cancer. In one study, researchers looked at how cannabinoids work together, and found that CBGA and THCA team up to fight colon cancer cells. When they worked together, the cannabinoids stopped the cancer cells from growing and sped up their death.
As can be seen through this discussion, CBGA cannabinoids not only add to the entourage effect, they also have some unique attributes that can produce positive health outcomes. Whether you are looking to increate the potentiality of your THC products or are suffering from disease, look for products that contain CBGA to drastically improve the quality of your health and wellness.
A convenient and precise way to incorporate our blends into your wellness routine. Our tinctures and capsules are carefully formulated to provide targeted support.
For those looking for faster-acting effects and robust flavor profiles, our carts and wax concentrates offer a potent and flavorful experience.
Boost your daily ritual with our potent and rare NeuroLeaf tea blends, artfully created to combat specific issues and found nowhere else but here.
Our premium terpene selections allow you to fine-tune your taste bud experience, or enhance certain medicinal benefits.


🌿 Unlocking the Wonders of CBDv: A Deep Dive into its Effects and Benefits 🚀 As we journey through the vast landscape of cannabinoids, let’s shine
Exploring Aloysia gratissima Introduction Aloysia gratissima, commonly known as Whitebrush or Bee-brush, is a native plant of the Americas, revered for its medicinal and aromatic
Cannabidivarin (CBDV) is making waves in the wellness world as a non-intoxicating cannabinoid with promising benefits for brain health, inflammation, and overall balance. Endocannex’s Zen Mastery Tincture delivers 10 mg of CBDV per dose, offering a gentle introduction to this powerful compound. Here’s what you can expect in terms of effects over the short, medium, and long term.